Welcome to Aquaponics
Welcome to the world of aquaponics, where nature’s harmony powers a sustainable and efficient way to grow food. Picture a system where fish and plants thrive together—each supporting the other’s growth in a closed-loop ecosystem.
Experience the satisfaction of nurturing life while creating your own fresh food supply.
This guide from Genetics Growers will walk you through everything you need to know to build your first aquaponics system, from choosing the right fish and plants to designing a setup that maximizes productivity.
Whether you’re just starting out or already have a green thumb, aquaponics offers a powerful, eco-friendly method of cultivation. At Genetics Growers, we’re here to support your journey with expert advice, practical tips, and community support. Ready to dive in?
It’s not just gardening—it’s a lifestyle shift toward sustainability and self-reliance.
How Aquaponics Works
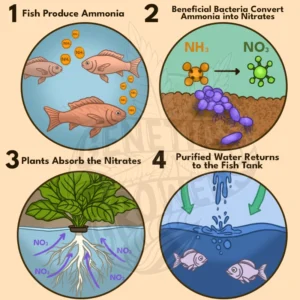
Aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) to form a sustainable, closed-loop food production system. Fish waste, rich in ammonia, is broken down by beneficial bacteria into nitrates that nourish plants. In turn, the plants purify the water, which cycles back to the fish tank.
Key System Components
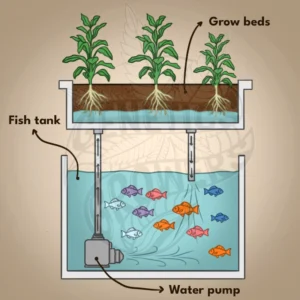
Every aquaponics system includes three main components: a fish tank, grow beds, and a water pump. The fish tank houses the fish; the grow beds support plant roots and beneficial bacteria; and the pump keeps water and nutrients flowing throughout the system.
One of the greatest advantages of aquaponics is its flexibility. Systems can be scaled for apartments, backyards, or commercial farms. Common fish include tilapia, catfish, and koi. Lettuce, basil, and tomatoes are popular plants thanks to their fast growth and nutrient needs.
Imagine transforming your balcony or backyard into a lush mini-farm.
Why Aquaponics?
Aquaponics conserves up to 90% more water than traditional gardening, thanks to its recirculating design. It eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, relying solely on fish waste for plant nutrition.
These systems work in diverse environments, enabling year-round food production whether you live in a city apartment or a rural homestead. Their sustainability and low environmental footprint make them ideal for tackling food security challenges worldwide.
A System Rooted in History
Aquaponics isn’t new. Ancient civilizations like the Aztecs used floating gardens that mimicked aquaponic systems. Over time, technology has refined these ideas into practical, modern solutions.
Today, aquaponics appears in urban farms from New York to Chicago, helping communities access fresh food while reducing environmental impact. What once sustained ancient civilizations can now empower modern growers like you.
Getting Started: Your First Setup
Starting your own aquaponics system is exciting. To succeed, you’ll need to understand three key components: the fish tank, grow beds, and water pump. Choosing wisely sets the stage for long-term success.
The fish tank is the heart of your system. Choose its size and material based on the fish species and quantity you plan to raise. Food-grade plastic or glass tanks are durable and safe. A good rule of thumb is one gallon of water per inch of fish. For beginners, tilapia or goldfish are excellent options.
Looking for high-quality seeds, growing supplies, or expert guidance? Explore Genetics Growers’ curated resources to start strong and build your system with confidence.
Designing Effective Grow Beds
Grow beds absorb nutrients from fish waste and support healthy plant growth. Use safe materials such as untreated wood or food-grade plastic, and aim for a 1:1 ratio between tank and bed size. Expanded clay pebbles are ideal, offering excellent drainage while providing surface area for beneficial bacteria.
Circulation and Water Flow
A reliable water pump keeps your system running smoothly. It should be capable of cycling the tank’s full volume at least once per hour. Regular cleaning and inspection are essential, and having a backup pump is highly recommended in case of power outages.
Ready to take the next step? Discover Genetics Growers’ aquaponics tools and educational content designed for beginners and experienced growers alike.
Sustaining a Healthy Ecosystem
Consistent maintenance is key to a successful aquaponics system. Focus on water quality, fish care, and plant monitoring to maintain balance and prevent issues.
Check water parameters regularly, including pH (ideal range: 6.8–7.2), ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates. Use testing kits to track changes and adjust pH with safe substances like vinegar (to lower) or potassium hydroxide (to raise). Keep ammonia levels near 0 ppm to protect fish health.
Feed your fish a high-quality diet appropriate for their species and avoid overfeeding. Healthy fish are active and alert. If behavior changes, test the water immediately and quarantine sick fish to prevent contamination.
Think of your fish not just as part of the system, but as co-gardeners in your journey.
Monitor plant health for signs of nutrient imbalance, such as yellowing leaves or slow growth. Prune regularly and remove dead foliage. Use natural pest control methods like neem oil to protect plants without harming fish.
Final Reflections
Starting an aquaponics system means embracing a smarter, more sustainable way to garden. With proper care, you’ll grow fresh, clean food while conserving resources and supporting the planet.
Enjoy the pride of producing healthy food—while giving back to the Earth.
Your First Steps & the Community
Here’s how to begin:
- Start Small: Begin with a manageable system and scale up as you gain experience.
- Monitor Regularly: Keep an eye on water quality, fish health, and plant growth.
- Join a Community: Share experiences, troubleshoot challenges, and learn from fellow growers.
Find your tribe of growers who share your values and curiosity.