Are you ready to unlock the secrets to stronger plants and more abundant harvests? Whether you’re just starting your gardening journey or already an experienced grower, mastering nutrient management can transform your results. In today’s world—where every leaf, petal, and seed matters—understanding how to deliver nutrients effectively is the key to achieving lasting plant vitality.
At Genetics Growers, we’re passionate about helping people connect with the science and art of plant nutrition. Our mission is to give you the knowledge and confidence to build a thriving, sustainable garden ecosystem. Whether you care for a few pots on your balcony or manage an entire field, the principles remain the same: provide the right nutrients, in the right way, at the right moment.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), “farmers can save nearly $30 per acre on land receiving excess nutrients by optimizing fertilizer use, minimizing environmental impact, and enhancing crop performance.”
In this article, you’ll discover how soil composition, microorganisms, and innovative agricultural technologies come together to shape nutrient efficiency. You’ll learn how to adapt nutrient applications to meet the specific needs of each plant—so every drop of fertilizer contributes to growth, not waste. By the end, you’ll have the tools and insight to elevate your gardening practices to a professional level.
Understanding the Basics of Nutrient Management
To keep plants healthy, it’s essential to understand how nutrients work together to support growth. Nutrient management starts with knowing which elements your plants need, how much they require, and when to supply them. Doing this correctly helps maximize plant health and minimize environmental impact.
Organizations such as the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) and NC State Extension highlight the importance of balanced nutrient application—not just for plant productivity, but for the sustainability of the ecosystem.
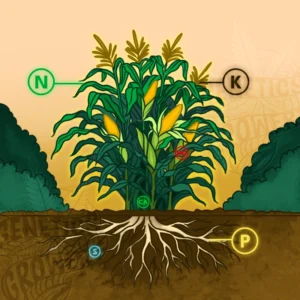
The Role of Essential Nutrients in Plant Growth
Plants rely on a variety of nutrients, classified as macronutrients and micronutrients:
- Macronutrients: (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) are needed in larger amounts. They drive photosynthesis, root development, and overall energy transfer.
- Micronutrients: (iron, manganese, zinc) are needed in trace amounts but are vital for enzyme activity and metabolic balance.
Key Nutrients and Their Functions:
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for leaf growth and photosynthesis.
- Phosphorus (P): Important for energy transfer and root development.
- Potassium (K): Helps in water regulation and disease resistance.
- Calcium (Ca): Crucial for cell wall structure and stability.
- Magnesium (Mg): Central component of chlorophyll.
- Sulfur (S): Integral to amino acids and proteins.
Balancing Nutrient Inputs with Crop Needs
True nutrient management isn’t about applying more—it’s about applying smartly. Matching nutrient applications to plant needs and environmental conditions prevents waste and promotes healthier growth.
The NRCS notes that implementing structured nutrient management plans can help farmers save up to $30 per acre while reducing the risk of runoff and improving soil quality. The key is timing and precision—providing what plants need when they need it most.
Environmental Implications of Improper Nutrient Management
When fertilizers are misused, excess nutrients can wash into waterways, fueling algae blooms and polluting ecosystems. Nitrogen and phosphorus are especially harmful when unbalanced.
The International Plant Nutrition Institute (IPNI) explains that “applying the right source of nutrients, at the right rate, at the right time, and in the right place ensures economic, social, and environmental sustainability.”
Following this framework helps ensure that nutrients are applied efficiently and responsibly, protecting both your plants and the planet.
Implementing Effective Nutrient Management Strategies
The 4Rs framework serves as a practical guide to achieving balance and efficiency in nutrient use.
1. Right Source: Choosing the Best Nutrient Inputs
Start with soil testing to understand what your plants really need. Choose fertilizers—organic or synthetic—that match those requirements. Compost and manure can offer rich, sustainable nutrient alternatives when applied properly.
2. Right Rate: Applying the Correct Amount
Avoid over-fertilization. Too much nutrient input can harm your soil and waste resources. Tools like Variable Rate Technology (VRT) help tailor applications based on data from soil analyses and previous yields.
3. Right Time: Timing Nutrient Applications
Timing is everything. Apply nutrients when plants can absorb them most effectively—often during active growth phases. Avoid fertilizing before heavy rain, and consider splitting applications across the season to maximize absorption.
4. Right Place: Ensuring Proper Nutrient Placement
Position nutrients where roots can access them directly. Methods such as injection or soil incorporation reduce nutrient loss and increase plant uptake.
By adhering to the 4Rs framework, you can implement effective nutrient management strategies that enhance plant health and protect the environment. For more detailed guidance, explore additional resources available on Genetics Growers.
Overcoming Challenges in Nutrient Management
Even with the best plan, growers face real-world challenges—from unpredictable weather to soil variability.
- Soil Variability: Different soil types within the same field can require unique nutrient treatments. Use GPS mapping and regular soil testing to fine-tune applications.
- Climate Change: Shifting rainfall patterns and droughts demand adaptive management. Practices like cover cropping and reduced tillage improve soil structure and water retention.
- Resource Constraints: Limited access to fertilizers can be offset by using organic amendments or partnering with local agricultural services for guidance.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, you can implement Nutrient Management Best Practices that promote plant health and environmental sustainability. For further guidance, explore more resources on Genetics Growers.
Empowering Your Nutrient Management Journey
Strong gardens start with strong foundations. By understanding nutrient dynamics and applying the 4Rs, you can achieve healthier plants and more sustainable practices.
Key Takeaways:
- Know your soil and understand the nutrients your plants need.
- Apply nutrients strategically using the 4Rs framework.
- Embrace technology and conservation methods to adapt to environmental change.
Ready to take the next step in your nutrient management journey? Explore more resources and expert insights at Genetics Growers. Join our community to share experiences, ask questions, and continue learning about the fascinating world of plant nutrition. Together, let’s cultivate a healthier and more sustainable future.